The Albanese government has finally set a 2035 climate course – and it’s a mission Australia must accept

The federal government has announced a long-awaited climate change target for 2035, committing to a reduction in emissions of between 62% and 70% below 2005 levels. Environmentalists claim the target is a failure, while some business groups and the opposition are likely to slam it as economic sabotage.
Setting a range target has two advantages. First, it provides flexibility to respond to whatever unfolds on the environment, technology or political front. Second, it avoids a frustrating political debate fixated on a single, precise future target.
Announcing the target on Thursday, Prime Minister Anthony Albanese said:
This is an ambitious but achievable target – sending the right investment signal, responding to the science and delivered with a practical plan. It builds on what we know are the lowest-cost actions we can deliver over the next decade while leaving room for new technologies to take things up a gear.
The target seeks to balance positive action with pragmatism. Achieving it requires a step-up in policies and implementation well beyond what has been achieved to date. This is a mission Australia must now accept.
A pathway to 2035
Climate change targets provide a clear vision of what the government is committed to delivering domestically. They are required under the Paris Agreement and affirm Australia’s membership of the global community.
The government announcement is aligned with advice delivered by the Climate Change Authority. That advice was delayed for months due to the election of US President Donald Trump – the policy repercussions of which the authority needed to consider – and the May federal election in Australia.
Last year, draft advice by the authority suggested an emissions reduction target of 65–75% by 2035.
More recently, a report from the Business Council of Australia claimed the cost of meeting a target above 70% was economically unacceptable.
If Australia is to meet its commitment to net-zero by 2050, and emissions fall in a straight line from 2030 to 2050, the 2035 target must be about 57%. Of course, this assumes that net-zero by 2050 is environmentally acceptable – which many, including the Grattan Institute, have argued is not.
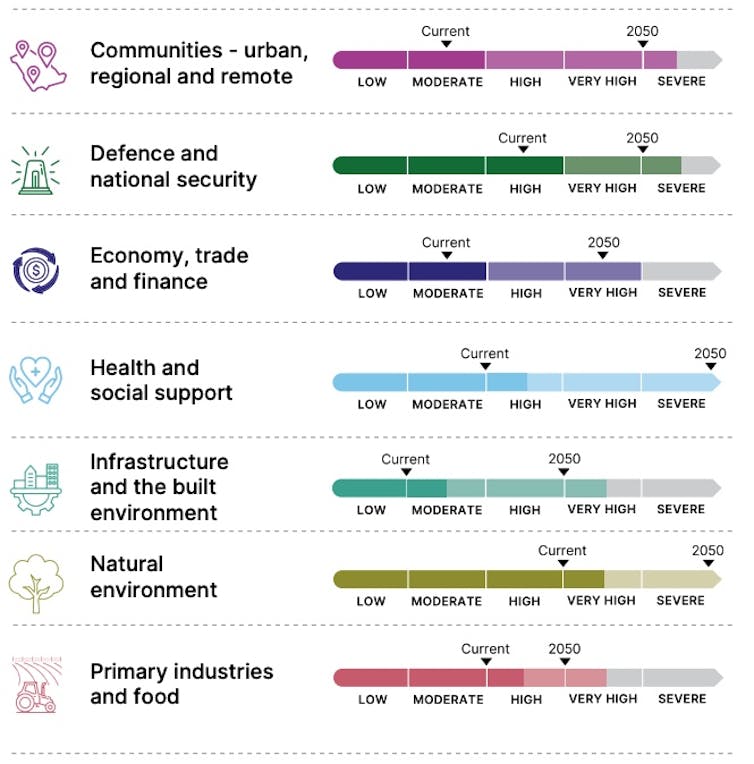
And this week, the government’s National Climate Risk Assessment outlined alarming damage if emissions are not dramatically curbed. All this suggests Australia must set the strongest possible target.
So has the government’s target hit the sweet spot? Let’s tease that out.
Deeper cuts this decade
Australia’s emissions target for 2030 is a 43% emissions reduction, based on 2005 levels. We currently emit 440 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent per year – 28% below 2005 levels.
To achieve the 2030 target, our annual emissions must fall by about 18 million tonnes a year. Meeting this target remains challenging. If the 2030 target is achieved, the annual rate of reduction would have to rise to 23 million tonnes or 33 million tonnes to meet the 62% or 70% target levels, respectively.
That’s why today’s targets are not lacking ambition. If the 2030 target is not achieved, then meeting the 2035 target – even the bottom of the range – only gets harder.
Disappointingly, however, the government has not clarified whether it’s essentially committing to 62% emissions reduction – with the option of greater ambition – or whether it will go for a 70% reduction but accept 62%. Or is it aiming for something in the middle?
The policy challenge ahead
Meeting the target will require progress across the economy – not just in the land sector and electricity generation, where most of the action has been to date. To achieve it, a major acceleration in government policy is needed.
So far, the Albanese government’s climate policy offering has been limited.
In 2022, the government established the Capacity Investment Scheme, which guarantees a certain revenue to renewable energy investors. It is designed to accelerate clean energy generation to meet Australia’s target of 82% renewables in the electricity mix by 2030. No further policy exists to reduce electricity emissions beyond that point.
The government also strengthened the Safeguard Mechanism, an innovation of the Abbott government to control emissions from heavy industry. And the New Vehicle Efficiency Standard (NVES) aims to drive down emissions from personal and small commercial vehicles. These policies must be ramped up to meet the 2035 target. The government has committed to reviewing the Safeguard Mechanism and the NVES, presumably to do just that.
Most of the light lifting in policy work has now been done. What’s needed now is policy to propel emissions reduction in harder-to-abate sectors of the economy – such as heavy vehicle transport and agriculture.
On Thursday, the government released a Net Zero Plan, along with blueprints for six major sectors of the economy outlining what needs to be done to get there.
Among other spending measures, it announced:
- A$5 billion in the National Reconstruction Fund to help industrial plants cut emissions
- $2 billion for the Clean Energy Finance Corporation
- $1.1 billion to encourage domestic production of clean fuels
- $40 million for kerbside and fast-charging of electric vehicles.
These are positive moves. But it’s still unclear how the government plans to integrate the policies with actually meeting the target.
Now the real work starts
Australia now has 2035 emissions targets and plans to meet them.
The target is a much-needed step on the path to net-zero, but it’s just the beginning. Delivering it will demand action across all sectors of the economy – and that work must start now.
The alternative – unchecked climate change – is not just irresponsible, but unthinkable.![]()
Tony Wood, Program Director, Energy, Grattan Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.